Introduction
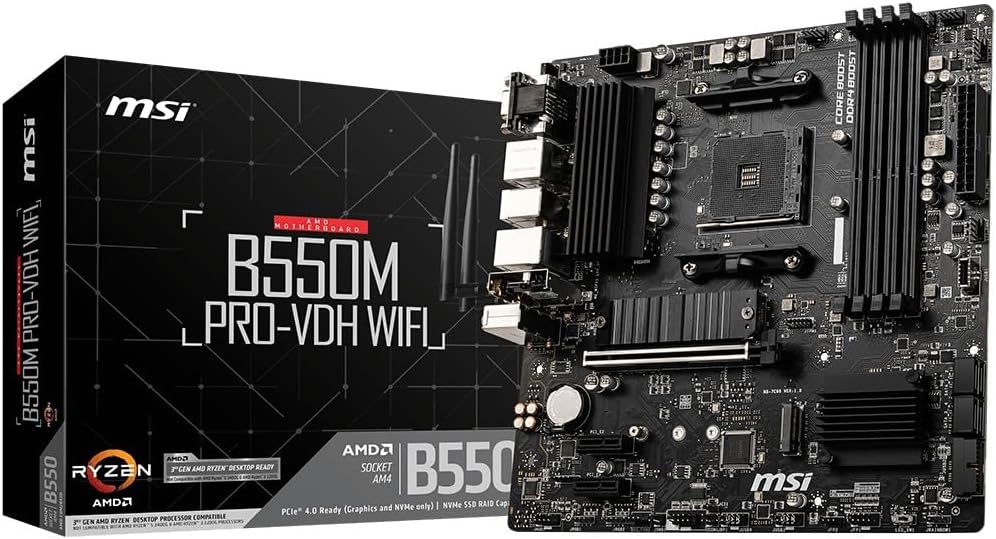
A computer motherboard serves as the central hub that connects all other components of a PC together, making it the foundation upon which every system operates efficiently. It acts not only as a physical platform but also as an intelligent controller for all communication between hardware parts such as CPUs, RAM, GPUs, and storage devices. Understanding why a motherboard is essential starts with knowing its basic functions and how these features impact overall performance.
The role of the motherboard in computer architecture cannot be overstated; it serves as the nerve center that coordinates data transfer, power distribution, and communication among all internal components. This centralization means that any bottleneck or inefficiency within the motherboard can affect the entire system's performance. Therefore, choosing a high-quality motherboard is crucial for ensuring smooth operation, optimal performance, and longevity of your computer.
Key Features of Modern Motherboards
A modern motherboard is equipped with several essential features that enhance its functionality and compatibility:
- Bios/UEFI Firmware: The Basic Input Output System (BIOS) or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) initializes hardware and loads the operating system. UEFI offers more advanced boot options, better security features, and improved user interfaces compared to BIOS.
- Chipset Quality: Determines how well the motherboard manages data flow between components like CPU and RAM, affecting overall performance and stability.
- Form Factor (ATX, Micro-ATX): Defines the physical size of the board which impacts space constraints within a case.
- Sockets: For CPUs, ensuring compatibility with specific processor types such as Intel's LGA 1700 or AMD’s AM4.
- RAM Support: Specifies supported memory types and capacities (e.g., DDR4 up to 64GB).
- Expansion Slots: For adding graphics cards, sound cards, network adapters, etc. Common slots include PCIe x16 for GPUs.
Pros and Cons of Modern Motherboard Designs
Motherboards come with a range of advantages and disadvantages that users should consider before making a purchase:
Pros
- Enhanced Performance: Better data management through improved chipsets.
- Increased Stability: Advanced BIOS/UEFI firmware provides robust hardware control and error handling capabilities.
- Customizability: Expandable slots allow for easy upgrades or additions of new components.
Cons
- Poor Compatibility: Mismatched sockets can render a motherboard incompatible with certain CPUs.
- Space Constraints: Smaller form factors like Micro-ATX may limit expansion options or cooling solutions.
- Higher Costs: High-end motherboards come at premium prices due to advanced features and materials.
Technical Specifications of Motherboards
The technical specifications of a motherboard are crucial in determining its capabilities. Key parameters include:
- CPU Socket Type: Determines which CPUs the board can support (e.g., LGA 1700 for Intel).
- RAM Support: Specifies supported memory types and capacities.
- Expansion Slots: PCIe, SATA ports, USB headers.
- Onboard Graphics/Network: Integrated solutions reduce the need for separate components.
Benchmarking Motherboards
Benchmarks provide objective performance metrics that can help in choosing between different models. Websites like PassMark and CpuBench offer detailed scores across various categories such as memory bandwidth, disk read/write speeds, and overall system responsiveness.
- Memory Bandwidth: Measured in GB/s (gigabytes per second).
- Disk Read/Write Speeds: Reflecting the speed of data transfer between storage devices and memory.
Real-World Usage Scenarios for Motherboards
The choice of motherboard greatly influences daily computing activities:
- Gaming Performance: A high-quality PCIe lane allocation ensures better graphics card performance.
- Multitasking Efficiency: Enhanced RAM support and multi-channel capabilities improve application switching speed.
Case Studies of Motherboard Impact on System Performance
Several case studies have demonstrated the significant impact a high-quality motherboard can make:
- Improved Overclocking Capabilities: A robust design allows for higher CPU frequencies, boosting performance.
- Better Power Management: Efficient power delivery systems minimize heat generation and improve stability.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Motherboards
Frequent problems include BIOS issues, compatibility conflicts, and hardware malfunctions. Here are some troubleshooting tips:
- Bios Updates: Keeping firmware up-to-date can resolve minor issues.
- Hardware Compatibility: Making sure all components work seamlessly together.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are some common questions and their detailed answers:
- What is the difference between ATX and Micro-ATX form factors?
- Answer: The primary distinction lies in size; ATX boards are larger, offering more expansion slots whereas Micro-ATX limits physical space but still provides sufficient connectivity.
- Why do some motherboards support multiple RAM channels?
- Answer: Multichannel memory architecture allows simultaneous data transfer across two or more sticks, significantly increasing overall bandwidth and improving multitasking capabilities.
- How does UEFI differ from BIOS?
- Answer: UEFI offers enhanced boot options, better security features, and improved user interface compared to traditional BIOS.
- What factors determine a motherboard's benchmark score?
- Answer: Benchmarks are influenced by several factors including memory bandwidth, disk read/write speeds, and overall system responsiveness.
- Why is power delivery important for motherboards?
- Answer: An efficient power delivery design ensures stable voltage supply to the CPU, thereby improving system stability and allowing better overclocking potential.
- How do I troubleshoot a motherboard?
- Answer: To diagnose issues, start by checking BIOS settings for updates or adjustments. Ensure all hardware components are compatible and properly connected.
- Can I upgrade my motherboard?
- Answer: Upgrading is possible but depends on your current build's compatibility. You may need to replace other components like CPU and RAM.
- What are the pros of using a high-end motherboard?
- Answer: The benefits include better performance, increased stability through advanced BIOS features, and greater customizability via expansion slots.